
A music composition technique where the musician utilizes recorded sounds (whether via reel-to-reel tape or digital recording), pitch-shifts them into multiple different notes, and sequences them together to form a melody. The sounds can be electronic in origin or absolutely anything audible enough for a microphone to pick up.
An early catchall term for electronically-produced sound effects, ambiance, and music.
An electronic music technique invented by Daphne Oram that involves drawing shapes onto clear 35mm film.
A diagram that electrical engineers use to describe the design of an electrical circuit.
A musical instrument that generates an electric tone, the pitch and volume of which is controllable via two respective antennae. Invented by Leon Theremin.
A electrical circuit that generates sound waves in various shapes. Also known as a tone generator.
A type of oscillator that produces a tone higher in pitch the more voltage is applied to it. Early Moog synthesizers used them, and they were commonly known to fall out of tune due to fluctuations in voltage, temperature, and humidity.
An electronic musical instrument made up of multiple oscillators, each capable of generating different waveforms. Some kinds of synthesizer play back prerecorded samples instead of generating a tone with oscillators.
A synthesis technique in which one waveform's frequency is modulated by another waveform. Famously used in the Yamaha DX7 synthesizer, the Sega Genesis, and certain early PC sound cards.
A communication standard designed to allow synthesizers to send data between themselves, and also to and from computers. MIDI stands for Musical Instrument Digital Interface.
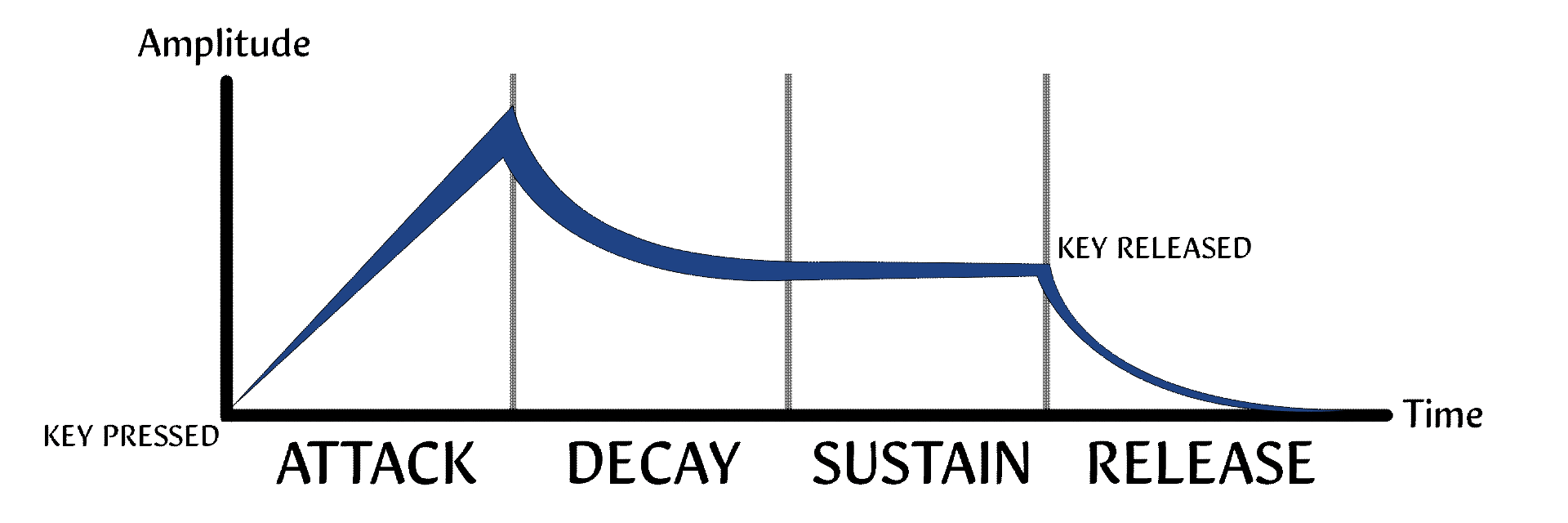
A visual representation of a sound's volume over time. ADSR stands for attack, decay, sustain, and release.
An short digital audio clip, used as an instrument in a tracker, a DAW, or a synthesizer that supports sample playback.
A computer program with which a musician can compose a sequence of notes, with either simple waveforms, FM synthesis, or sample-based instrumentation, depending on the tracker used. Commonly, the workflow resembles a grid of commands. Some popular trackers are OpenMPT, FamiTracker, Deflemask, and Renoise.
A computer program with which a musician can compose MIDI data to be sent to a synthesizer, or to be played
by their computer's internal synthesizer. Commonly, the workflow resembles a roll from an old player piano.
Musicians in the 1990s and early 2000s used Cakewalk, and
a popular modern equivalent is Sekaiju.
A modern kind of sequencer that can load virtual instruments and record audio from a microphone or a real instrument. Musicians or music producers can use programs like this to fully mix and master a modern song. Some popular DAWs include FL Studio, Reaper, and Ableton Live.